Steering Through California’s 2024 Labor and Compliance Changes

- By Harri Insider Team | March 28, 2024
In a recent webinar hosted by QSR magazine, industry leaders delved into the evolving compliance regulations in California, highlighting their impact on businesses statewide and across the United States.
Anthony Zaller, Partner at Zaller Law Group, provided a comprehensive overview of some of the hurdles faced by the operators in California from a legal perspective as these changes take place in 2024.
AB 1228: Navigating the New Wage Landscape for Fast Food Operators
Starting April 1, 2024, a significant shift will occur in the wage structure for employees at national fast-food chains in California. The legislation mandates a minimum wage increase to $20 per hour, with subsequent annual adjustments based on the consumer price index or by 3.5%, whichever is less. This new law imposes a minimum salary requirement of $83,200 to qualify an employee as exempt.
Under California law, to qualify as an “exempt employee” for wage and hour purposes, you must receive a salary of at least two times the state minimum wage for someone working 40 hours a week and meet other specific requirements.
“I’ve got a lot of clients reassessing that,” Zaller notes. “They can’t pay that high salary threshold to qualify the employee as an exempt employee. They’re just switching the employee to hourly and complying with overtime meal and rest break requirements.”
To manage these changes effectively, automated scheduling systems and data analytics become invaluable to operators. By reducing overtime expenses and allowing for precise labor demand forecasting, aligning staffing levels more effectively aligns with business needs.
To help operators navigate these wage increases, Harri offers an advanced workforce management platform. This platform simplifies compliance through automated scheduling, ensuring that labor costs are optimized without sacrificing service quality. Harri’s platform also offers real-time labor analytics, allowing operators to make informed staffing decisions that adhere to the new wage regulations.

The 2024 Statewide Minimum Wage Increase in California
Zaller also highlighted the upcoming statewide minimum wage increase, setting the stage for all employers in California to raise the minimum wage to $16 per hour for non-exempt employees starting January 1, 2024. With a ballot initiative in November 2024 to potentially increase it further to $18 over time, operators must prepare their budgets for these incremental wage increases.
Conducting a thorough wage audit is essential to ensure all employees are compensated according to the new standards, taking into account any local ordinances that might stipulate a higher minimum wage. By investing in employee training and development, operators can enhance productivity and mitigate the turnover costs associated with the hiring and training of new staff, presenting a cost-effective strategy to adapt to the wage increase.
Enforcing schedule adherence is also essential for controlling labor costs and for complying with labor laws and regulations. Harri’s software takes into account regional and localized labor laws, ensuring that schedules align with compliance requirements. By automating compliance management, operators can avoid penalties and legal issues associated with non-compliance, further reducing labor costs.
Updated Food Handler Card Requirements in California
The updated regulations also address food handler card requirements, mandating that employees obtain certification within 30 days of their hire date. Employers are now responsible for covering the $15 cost of training and examination, in addition to compensating employees for the time spent obtaining the certification.
To streamline compliance, operators should develop a checklist to ensure all new hires meet the certification requirements within the mandated time frame. Hosting in-house training sessions can further simplify the process while negotiating group rates for certification can significantly reduce the costs associated with compliance per employee.
Safeguarding Your Business Against PAGA Claims in California
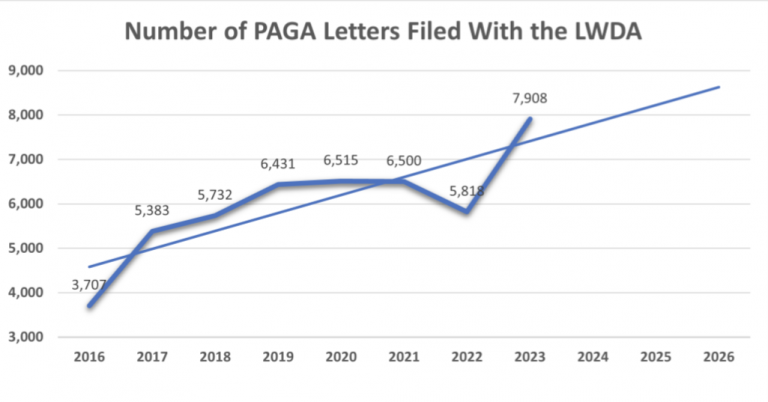
Protecting against claims under the Private Attorney Generals Act (PAGA) is a priority for many operators, especially after a recent ruling prohibiting courts from dismissing claims due to ‘unmanageability.”. Since its effective date in 2004, PAGA has allowed private individuals to bring representative actions, posing a potential risk for businesses.
The potential costs associated with PAGA claims are prompting operators to find ways to protect their businesses. “The penalties range from $100 up to $200 per employee, per pay period,” shared Zaller. “The damages get very large very quickly for multiple violations that are alleged to occur by the plaintiff’s attorney.”
To mitigate this risk, implementing an arbitration agreement with a class action waiver is advised, alongside regular audits of wage and hour policies. Additionally, training frontline managers on compliance can not only reduce the likelihood of costly legal violations but also ensure the business operates within the confines of the law.
While these regulatory updates present challenges, they also offer operators a chance to refine and strengthen their operational approaches, aiming for cost mitigation and enhanced profitability. Establishing comprehensive systems and processes now helps businesses to adeptly manoeuvre through California’s evolving regulatory landscape, effectively minimizing potential costs and paving the way for sustainable operations.