Essential Updates on Labor Regulations: Compliance Advisory Q1 2025

- By Harri Insider Team | March 26, 2025
Disclaimer: Please note this advisory is intended for summary purposes only. Any guidance or materials provided do not constitute legal advice and cannot be substituted for the advice of legal counsel.
Los Angeles County Fair Workweek Ordinance
On April 23, 2024, the Los Angeles County Board of Supervisors voted to implement a fair scheduling ordinance, which will go into effect on July 1, 2025. The ordinance applies to retail employers with 300 or more employees worldwide, including franchises and temporary staffing agency workers, that operate in unincorporated Los Angeles County. It covers employees who work at least two hours a week within these areas and are entitled to minimum wage and overtime under California law.
Key Requirements:
- Good Faith Estimate of Work Schedules
- Advance Notice of Work Schedules
- Access to Additional Hours for Current Employees
- Predictability Pay for Work Schedule Changes
- Rest Between Shifts
Non-compliance can lead to severe consequences including fines of up to $500 per violation, with penalties increasing to over $1,000 for retaliation. Employers may also be subject to administrative fines of up to $500 per violation, with higher penalties for repeat offenses.
Employees who experience violations of the ordinance may recover unpaid wages, penalties, reinstatement, and legal fees as remedies under the ordinance.
Salary Transparency
In our last compliance advisory, we highlighted several U.S. states that enacted salary transparency laws in 2024. Below is a summary of those set to take effect in 2025:
Massachusetts
- Legislation: H.4890
- Effective date: October 29, 2025.
- Requirements: Employers with 25 or more employees in Massachusetts must include the pay range (annual salary range or hourly wage range) in all job postings and internal postings for promotions or transfer to positions with different responsibilities. Employers must provide the pay range to current employees and applicants upon request. Employers must maintain records related to pay transparency for all job postings and internal opportunities.
New Jersey
- Legislation: SB2310
- Effective Date: June 1, 2025
- Requirements: Employers with ten or more employees must disclose the hourly or salary range and provide a general description of benefits and other compensation programs available for the position in all internal and external job postings.
Vermont
- Legislation: H. 704
- Effective date: July 1, 2025
- Requirements: Employers with five or more employees must include compensation details in job advertisements for positions in Vermont or remote positions supporting Vermont-based offices. Advertisements must disclose the compensation or a range of compensation for the position. For tipped positions, employers must disclose the base wage or range of base wages, excluding tips. On December 31, 2024, the Attorney General’s Office published guidance for employers and employees regarding the new law on its website, which can be accessed here: Final Version of H 704 Guidance (12-31-2024).pdf.
Given the upcoming wage transparency requirements, it is crucial for employers to review their active job descriptions. Updates to pay transparency laws may necessitate a minimum and maximum hourly or salary compensation in any advertisement for an opportunity for a job, promotion, transfer, or disclosure at a particular point within the hiring process. Please review your jurisdiction’s specific requirements to ensure compliance.
Please refer to the Harri Knowledge Base articles on Job Template Management and Editing Job Posts (must be signed in to Harri to view) to adjust your job description compensation requirements.
Michigan Minimum Wage Increase Took Effect on February 21, 2025
On February 21, 2025, Michigan’s minimum wage increased to $12.48 per hour following a Michigan Supreme Court ruling that reinstated a previously approved wage schedule.
This increase was in addition to the standard annual adjustment that took effect on January 1, 2025. It’s crucial that employers have already updated their payroll processes and ensured compliance with the new wage requirements. If not, immediate action is necessary to align with the updated law and avoid potential penalties.
For further guidance on compliance, employers should review Michigan’s wage laws or consult with legal and payroll professionals.
California Considering Fast Food Minimum Wage Increase
Following its second meeting of 2025, the California Fast Food Council is considering a $0.70 increase to the state’s fast food minimum wage. The council plans to discuss this proposal at a future meeting, though a date has not yet been set.
Employers should start planning for the potential rise in overtime costs. Under the new rate, overtime pay will amount to $31.05 per hour, while double overtime pay will increase to $41.40. The higher minimum wage will also impact the salary threshold for exempt employees. To maintain exempt status, employees must earn at least twice the minimum hourly rate multiplied by 2,080 hours per year. If the wage rises to $20.70 per hour, the new minimum salary for employees in fast-food businesses will be $86,112 annually.
If the increase is approved, fast-food operators will need to update employee notices to comply with Labor Code section 2810.5 and ensure pay stubs accurately reflect the updated hourly rate and overtime calculations.
It is our commitment to keep you informed about the latest developments. We will continue to monitor developments and provide updates as more information becomes available.
Harri users may update the minimum wage under General Workforce Management Settings.
Certain states mandate the use of a notification form to inform employees of any changes to their wage rate. If your business operates in one of these states and you are utilizing our Onboarding service, you can make the process seamless by using our Bulk Pay Rate Notice tool, conveniently located in the My Docs section of Harri. With it you’ll be able to:
Select a large group of employees and send wage rate notice to a group (instead of individuals)
- Customize your view with filters to show who has signed
- Sync the updated wage to TeamLive employees (if applicable)
Florida E-Verify Legislation
Florida legislators have introduced three bills (SB 782, HB 1033, and HB 955) to expand the state’s E-Verify employment eligibility requirements significantly. These bills eliminate the current 25-employee threshold, requiring all private employers to use E-Verify regardless of size and broadening the definition of “employee” to include independent contractors. They also transfer the administration and enforcement of E-Verify from the Florida Department of Law Enforcement to the Department of Commerce’s Office of Economic Accountability and Transparency. The bills authorize law enforcement agencies to use the E-Verify system to investigate the immigration status of detained individuals and are slated to take effect July 1, 2025, pending approval.
I-9 Best Practices
- Conduct periodic internal reviews using Harri to ensure all records are complete and up-to-date.
- Train system users on best practices for Form I-9 management within the platform.
- Use reporting features to monitor retention timelines and maintain compliance.
By leveraging Harri’s Form I-9 functionality, employers can more efficiently manage audits and inspections while better ensuring compliance with federal regulations. For additional assistance with using Harri’s Form I-9 tools, please contact our support team.
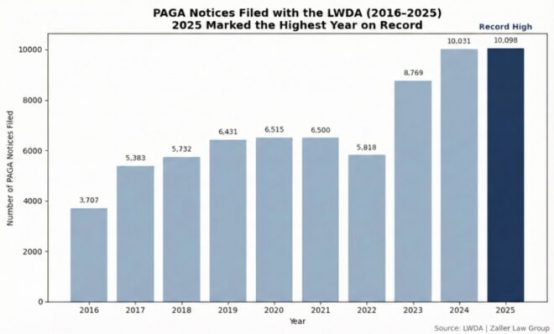
PAGA
California’s 2024 PAGA reform created a huge opportunity for restaurant operators to reduce their legal risk. To take advantage, employers must demonstrate reasonable efforts to comply with the Labor Code.
Employers may qualify for penalty reductions of up to 85 percent if they demonstrate efforts to comply with labor laws before receiving a records request or notice of PAGA violation(s). Further, penalties may be reduced by up to 70% if employers take corrective measures upon receiving a notice of PAGA violation(s).
The legislation also limits penalties to $50 per pay period for isolated violations lasting fewer than 30 consecutive days or four pay periods and additionally clarifies that heightened penalties of $200 per pay period only apply when an employer acts maliciously or when a court or agency had previously found an employer’s practices unlawful within the preceding five years.
Employers can further avoid penalties by curing violations concerning wage statements, meal/rest period premiums, overtime, minimum wage, and expense reimbursement.
In sum, there are now a variety of ways for an employer to drastically reduce and sometimes even potentially eliminate penalty amounts.
This may include but is not limited to
- Implementing a compliance monitoring system
- Establishing a regular audit schedule
- Creating documentation procedures
- Training managers on corrective actions
- Setting up violation response protocols
FLSA Exemption Standard Update
On January 15, 2025, the U.S. Supreme Court issued its decision in E.M.D. Sales, Inc. vs. Carrera, addressing the standard of proof an employer must meet when claiming that a worker is exempt from minimum wage and overtime pay under the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA). The court ruled that the appropriate standard is the preponderance of the evidence, the standard typically applied in civil cases, rather than the more demanding clear and convincing evidence standard used by the Court of Appeals for the Fourth Circuit. This ruling provides clarity for employers on the standards that courts apply when employers assert that employees are exempt from minimum wage and overtime under the FLSA. Nevertheless, regular classification audits, payroll alignment, and proactive workforce planning will help reduce legal risks and labor costs.
Ohio Pay Stub Protection Act
Effective April 9, 2025, Ohio employers must provide employees with a written or electronic earnings statement each pay period. The statement must include key details such as the employee’s name, address, employer name, gross and net wages, deductions, pay period dates, and for hourly employees, hours worked, hourly wage rate, and overtime hours. Employers should ensure their payroll systems meet these new requirements.
Harri, your partner in compliance
As employment regulations continue to evolve, Harri stands by your side, ready to assist in managing these changes. Recognized for our expertise in employer technology solutions, we focus on equipping you with the necessary tools and insights to support your compliance efforts. Choose Harri as your partner in compliance.